Stamp Staff
Are You Feeling Overwhelmed?
Get 20 Hours of Your Week Back... Guaranteed!
You can focus on what matters most with Virutal Assistants who are individually trained on our proven 7 to 8 figure systems and processes
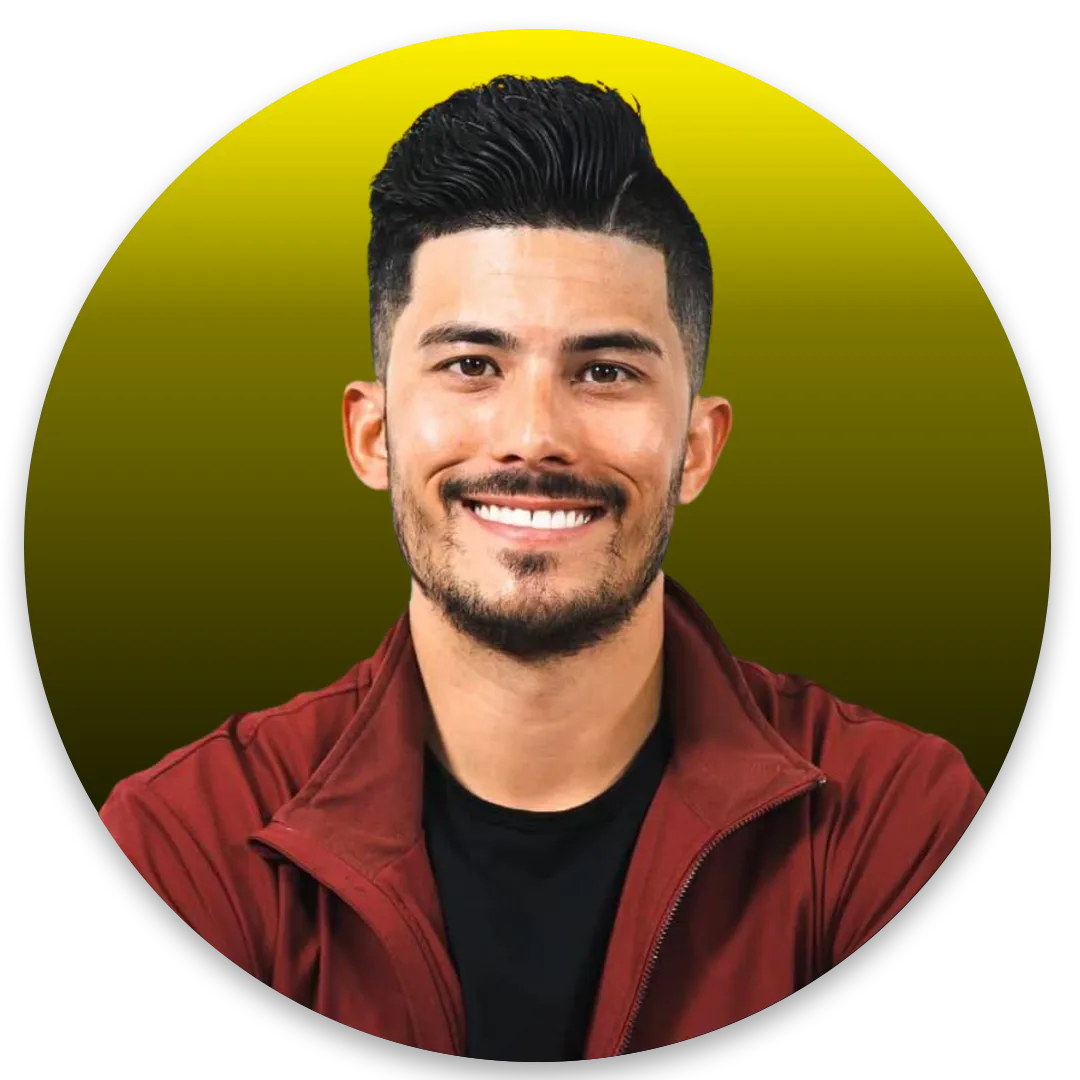


"You guys have to use Stamp Staff! Kristin and Mark are awesome. I've known them for over 5 years and they've been amazing. They've helped me, they've helped many people in my community. If you need VA's, if you need help in your business they are the people to go to."
Ryan Pineda, Founder of Pineda Co
What Could You Do With an Extra 20 - 40 Hours per Week?

The Solution to Save Time Begins Now
While we handpick and prepare your perfect match, our elite in-house team of executive assistants (think of them as your personal Productivity Task Force) will immediately get to work — clearing your backlog, managing your inbox and calendar, and handling personal tasks so you start reclaiming your time from day one.
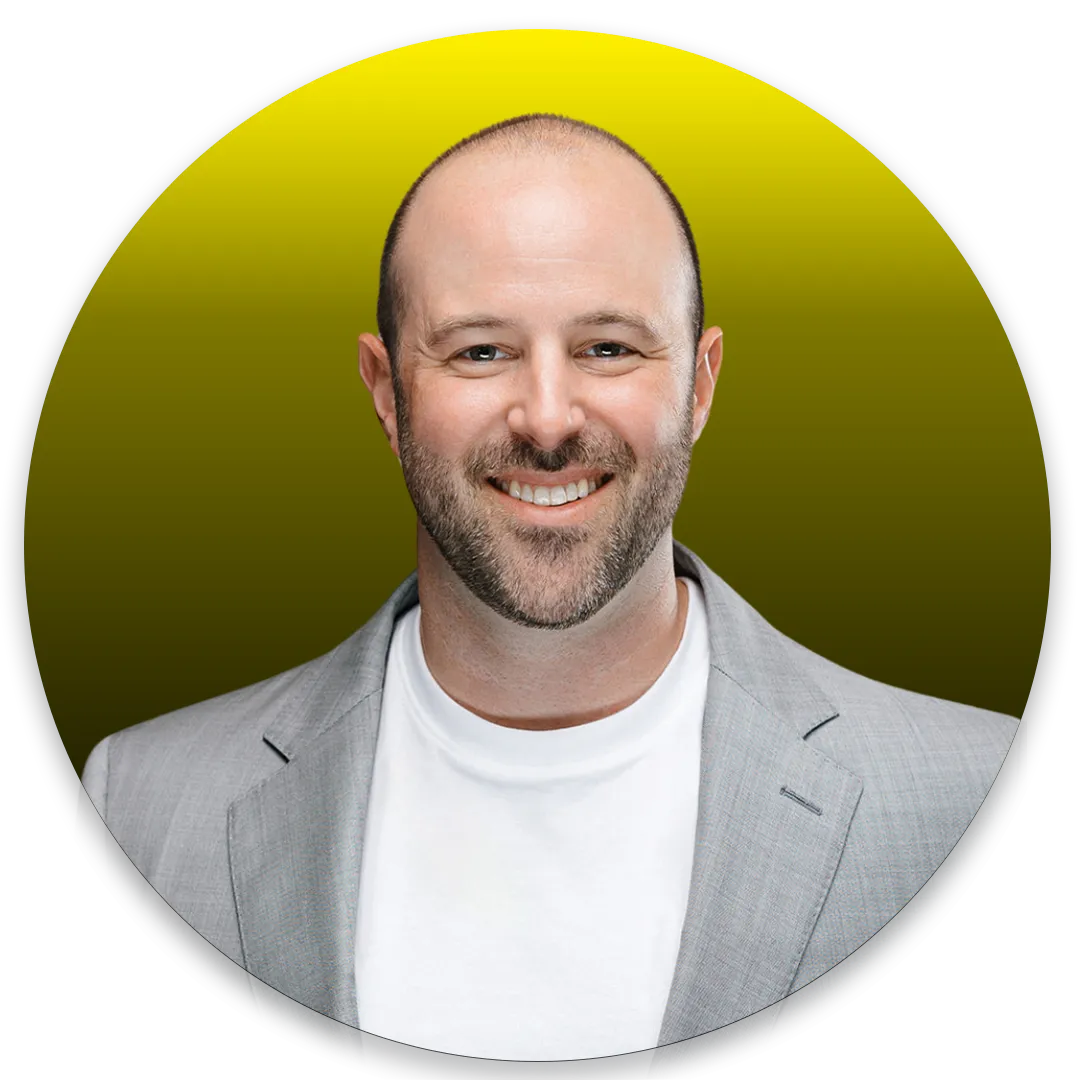


"I've been so incredibly happy working with Stamp Staff! I have our social media team member doing daily social media posts, email newsletter, lead page build out and more. It helped my lead generation 10x!"
David Menapace, President of Launchpad Consulting LLC
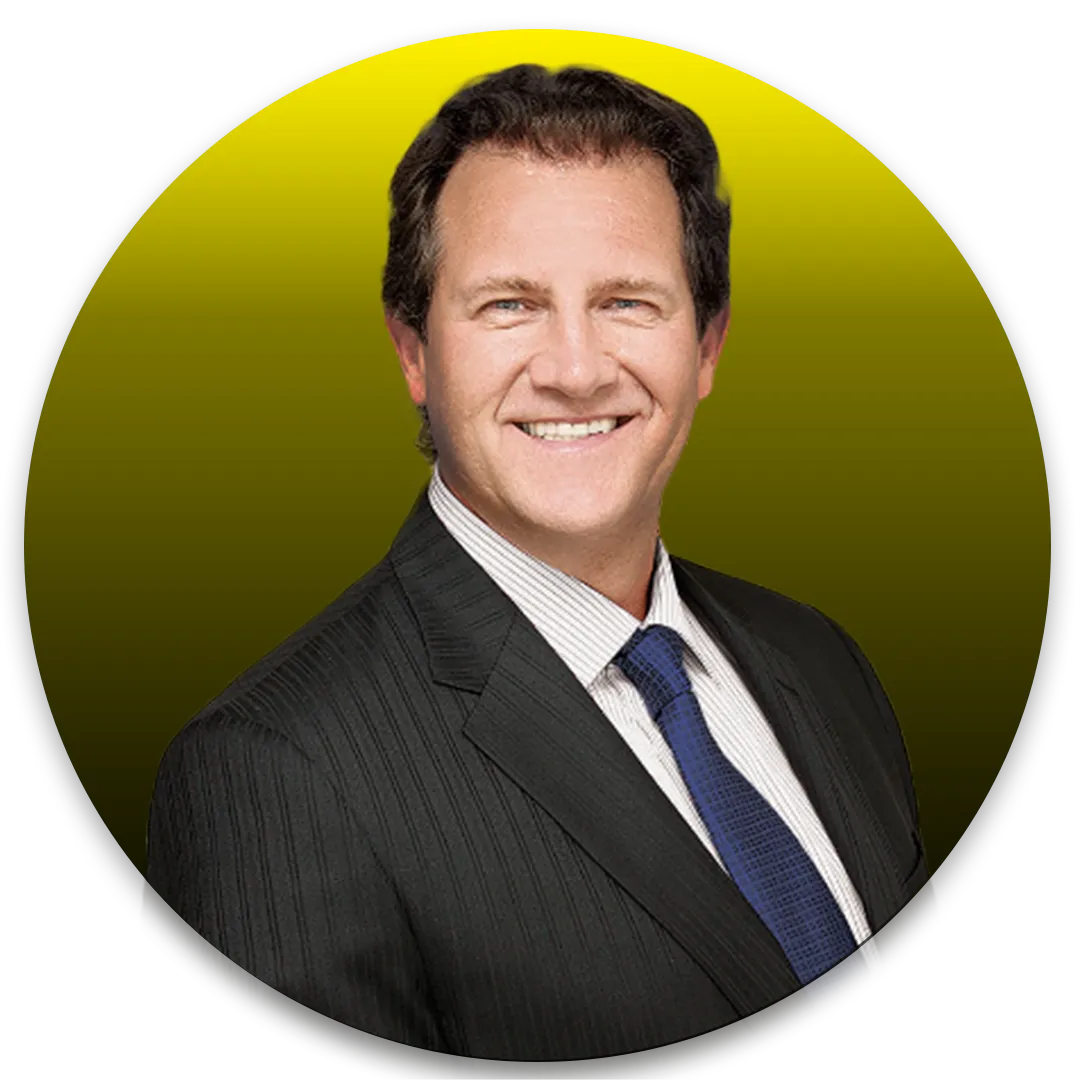


"I also use Kristin Stampini's Virutal Assistant and they're really really good. Kristing and Mark's Virtual Assistants understand the Craig Proctor System, they understand real estate."
Craig Proctor, Founder and CEO of Craig Proctor Coaching
What Stamp Staff Can Do For You
-
Digital Marketing Maintain brand visibility across platforms.

-
Social Media Management Plan, schedule and analyze content.

-
Brand Management Manages brand consistency and growth.

-
Video Editing Craft engaging promotional videos.

-
Graphic Design Create branded visual assets professionally.

-
Google Business Profile Optimize local listings & visibility.

-
Analytics & Reporting Performance data for better decisions.

-
Newsletter System Build and send email newsletters.

-
Blogging Publish content for SEO and branding.

-
Outbound Calls Make outbound calls.

-
Inbound Calls Make inbound calls.

-
Lead Management Nurture and warm up the leads.

-
Feedback Management Collect and process customer feedback.

-
Issue Identification Respond to concerns promptly.

-
Appointment Management Schedule and confirm meetings.

-
Data Analysis Insights to help you convert more.

-
Database Integration Keep your data organized and synced.

-
Document Preparation Prepare and create document.

-
Email Management Manage and organize emails.

-
Personal Assistant Supports personal & admin needs.

-
Data Entry Keep your information accurate and updated.

-
Travel Arrangements Book flights, hotels, and itineraries.

-
Customer Support Assist clients and resolve inquiries.

-
Market Research Find information and compile summaries.

-
Document Prep Create professional forms and templates.

-
Travel Arrangements Book flights, hotels, and itineraries.

-
Customer Support Assist clients and resolve inquiries.

-
Inbox Management Keep your email organized and efficient.

-
Research Tasks Find information and compile summaries.

-
Reels Creates scroll-stopping reels

-
Shorts Creates scroll-stopping shorts.

-
Thumbnail Designs eye-catching thumbnails.

-
Podcast and Long Form Edits episodes & full videos.

-
Video Editing Spotlight
We’re proud to showcase our editing work for Jared Jones on TV – a YouTube channel full of dynamic real estate content, property tours, and lifestyle vlogs.
🔗 Visit YouTube Channel

Our Virtual Assistants are Trained for 120 HOURS
Know the difference!

Our 5 Steps Hiring Process to Filter Hundreds of Candidates to Find You the "THE ONE"
Only 3% make it through our process and 120 hours training. We'll give you top 3 candidates that are best match for your needs and character so can pick the BEST MATCH for you!
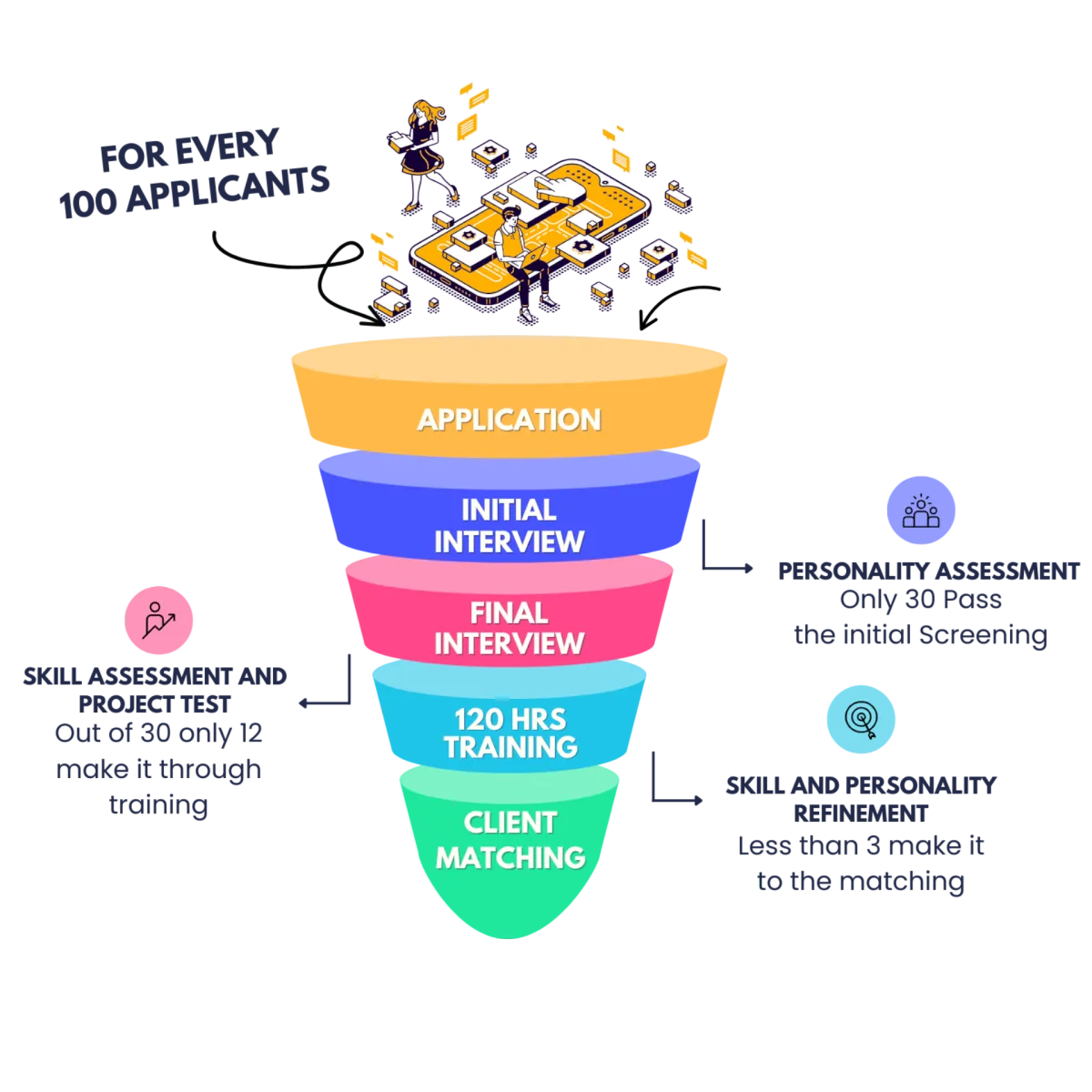

Stamp Staff Virtual Assistants:
Are equipped with proven processes that have supported the growth of 7 and 8+ figure companies
Read, write, and speak fluent english
Receive 1:1 and group training & mentorship, plus access to our community resources to continually bring more value to your business
Will work in YOUR timezone
Make sure you get 10-20+ hours back each week (starting with your very first week together!)
Our Happy Clients










Currently, We've Saved Our Clients 164,340 hours per year
AS SEEN ON
You Can Bring More Money But YOU CAN NEVER BRING BACK TIME!
Ready to free up your time?
Schedule a Free Discovery Call with us!
We will help you identify what help you need and give you some suggestions base on our assessment as a TEAM
We Will be Providing the BEST FIT for You
Stamp Staff is Only Hiring Virtual Assistants with experience, on top of their experience we train and equipped them that supports 7 and 8+ figure businesses
DECIDE HOW YOU WANT TO SPEND YOUR FREE TIME!!
Hire Full Time Assistant
Get 40 Hours a Week Back!
Starting at
$1,799/mo
Hire Part Time Assistant
Get 20 Hours a Week Back!
Starting at
$999/mo
You Can Call Us Anytime at
561-221-2292
STILL NOT SURE?
Frequently Asked Questions
Question 1: How do you vet and select your virtual assistants?
At Stampstaff, we have a rigorous screening process that includes skill assessments, experience verification, and behavioral interviews. We ensure our VA's meet high standards in professionalism, reliability, and expertise.
Question 2: What skills and experience do your VA's have?
Our VA's specialize in various areas, including administrative support, customer service, appointment setting, sales, social media management, and more. We match clients with VA's based on their specific needs and industry.
Question 3: Can I interview and choose my VA before hiring?
Yes! We provide you with pre-vetted candidates based on your requirements. You can interview them to ensure the best fit before making a final decision.
Question 4: Will my VA work exclusively for me, or do they handle multiple clients?
This depends on the package you choose. We offer full-time and part-time. We can match you with a VA who works exclusively for you.
Question 5: What happens if my VA is not a good fit?
If you feel your VA isn’t the right match, we’ll work with you to resolve any issues or provide a replacement at no additional cost. Our goal is to ensure a smooth and productive working relationship
Question 6: What tasks can your VA's handle?
We have dedicated conversion specialists, brand and content specialists, admin assistants, and more. If you have a specific need, let us know!
Question 7: Do your VA's work in a specific time zone, or can they adjust to my schedule?
Our VA's are available across different time zones and can match you with someone who aligns with your preferred working hours.
Question 8: How do you ensure productivity and accountability?
We have a structured monitoring system, regular check-ins, SOD and EOD reports, and performance tracking. We also encourage open communication between clients and VA's to ensure clear expectations and productivity.
Question 9: What are your pricing and contract terms?
Our pricing ranges from $999 to $1,899 per month, depending on how many hours you need your VA to work. We require a minimum 6-month contract to ensure stability and consistency in service. Let’s discuss your specific needs so we can recommend the best option for you.
Question 10: How does Stamp Staff support both clients and VA's during the working relationship?
We provide ongoing support, performance check-ins, and a dedicated Client Success Manager to ensure a smooth experience for both clients and VA's. If any issues arise, we step in to provide quick solutions.

FOLLOW US
LEGAL
Copyright 2026. Stamp Staff. All Rights Reserved.
84745 Old Hwy #15, Islamorada, FL 33036, United States
561-221-2292 | [email protected]